Plan Availability | All plan types |
Permissions |
|
Platform(s) | Web/Browser, Mac app, and Windows app (with some additional limited support on mobile) |
Note
If you are looking to parse out a datetime from a string, then use the
DATETIME_PARSE()function. Learn more here.For more information on
DATETIME_FORMAT, and other formulas, we recommend checking out the formula field support article.
Understanding the DATETIME_FORMAT function in Airtable
There are times when a date (and time) type field in your Airtable base needs to be formatted into another format outside of the available formatting options included within a date field’s configuration. In these instances, you can reference that date field in a formula field using the DATETIME_FORMAT function.
The DATETIME_FORMAT function will allow you to reformat the data from a date-type field into a string following your specifications. It follows this general structure:
DATETIME_FORMAT({yourDateTimeField}, 'format specifier(s)')
The format specifier allows you to dictate the structure of how your date should be returned. The format specifier can be something like 'DD-MM-YYYY,' 'YYYY/MM/DD,' 'MM.DD,' etc. For a full list of supported format specifiers, please see this article.
See below for a quick example of how DATETIME_FORMAT can transform a date field from one format to another.
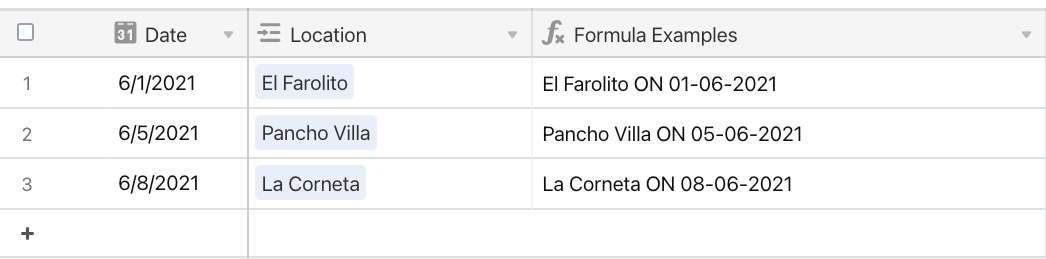
{Location} & " ON " & DATETIME_FORMAT({Date}, "DD-MM-YYYY")
Notice how we transform the date's format (MM/DD/YYYY) from the Date field to the Formula Examples field (DD-MM-YYYY ) above.
Reformatting a date for use in a primary field
Since the primary field in a table should contain a unique value for each record, a formula field is often used to help ensure this. The example below shows how to combine static text and a formatted date field’s value to create unique names for each record.
Let’s say your primary field’s formula is currently CONCATENATE("Experiment #", {Test ID}) . Here’s what that would look like in Airtable:

Using the autonumber value does create a unique name for each record, however, you want the experiment name to be slightly more complex so that it is less predictable and can be dynamically changed depending upon the value in the date field. Your table currently has the following fields:
“Experiment Name” - The primary field, which is a formula, for this table that concatenates the word "Experiment #" and the Autonumber field (Test ID).
Test ID - An autonumber field currently tracking our unique experiments.
Test Date - A date field that tracks the date on which an experiment took place. We want to leverage this field instead of the “Test ID” field.
We'd now like to update the Experiment Name field to include the date and time each experiment occurred. If you add a date field to a formula without using the DATETIME_FORMAT function, the formula will display both the date and time in a simplified ISO formatting. If your table is going to used and read by people, you'll probably want to alter your date to be a little more human-friendly.
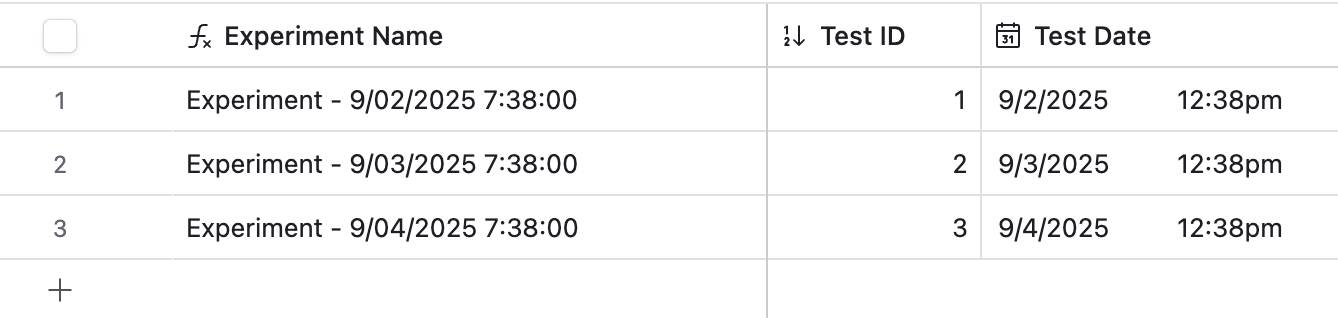
Here is what our “Test Date” field looks like without using DATETIME_FORMAT or any format specifiers CONCATENATE("Experiment #", {Test Date})):

That’s not very easy on the eyes. So let’s update the output slightly using the DATETIME_FORMAT function with some specifiers:
CONCATENATE("Experiment - ", DATETIME_FORMAT({Test Date},'M/DD/YYYY h:mm')
This will result in a more readable, but still unique experiment name for each record:
Understanding how to fix a timezone difference in your formula’s output
Occasionally, you may encounter a problem in which the timestamps in the DATETIME_FORMAT are offset to GMT or some other timezone. You may have noticed in the examples above that the times do not match. You can fix this problem in one of two ways:
The easiest way is by checking the "Use the same time zone (GMT) for all collaborators" in the date field's configuration menu. This can sometimes have downstream effect though. In those cases, use option 2.

A slightly more difficult, but more flexible way is to use the
SET_TIMEZONEfunction inside of yourDATETIME_FORMATfunction. A complete list of Airtable's supported timezone identifiers can be found here. You could use this formula instead if your team is all located in the PST time zone:CONCATENATE("Experiment - ", DATETIME_FORMAT(SET_TIMEZONE({Test Date}, 'America/Los_Angeles'), 'M/DD/YYYY h:mm')). This will lead us to the same, consistent, results: